Rinku Engineers is a well-established and trusted centrifugal pump manufacturer and centrifugal pump supplier in Ahmedabad, bringing more than 25 years of proven experience in designing and delivering reliable fluid handling solutions. Operating under the recognized AYUSH brand, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance centrifugal pumps that are engineered to meet the demanding requirements of modern industrial processes.
Our centrifugal pumps are designed to handle a wide variety of fluids including clear liquids, corrosive chemicals, acids, alkalis, hydrocarbons, edible oils, water, mud, and sludge. Each pump is developed using precision engineering techniques, high-grade raw materials, and strict quality control standards to ensure consistent performance, durability, and efficiency. The robust construction and optimized hydraulic design of our centrifugal pumps allow them to operate smoothly even under continuous and heavy-duty working conditions.
As a quality-focused centrifugal pumps exporter in Ahmedabad, Rinku Engineers supplies pumping solutions to customers across India as well as international markets. We understand the importance of reliability, energy efficiency, and long service life in industrial pumping operations, which is why our centrifugal pumps are thoroughly tested for performance, pressure, and durability before dispatch. From chemical and pharmaceutical industries to water treatment, food processing, textile, and heavy engineering sectors, our centrifugal pumps have been successfully installed in a wide range of applications.
With strong technical expertise, modern manufacturing facilities, and a customer-centric approach, Rinku Engineers continues to be a preferred choice for businesses seeking dependable centrifugal pump manufacturers and suppliers in Ahmedabad. Our commitment to quality, timely delivery, customized solutions, and professional after-sales support has helped us build long-term relationships with clients who rely on AYUSH centrifugal pumps for safe, efficient, and uninterrupted fluid handling operations.

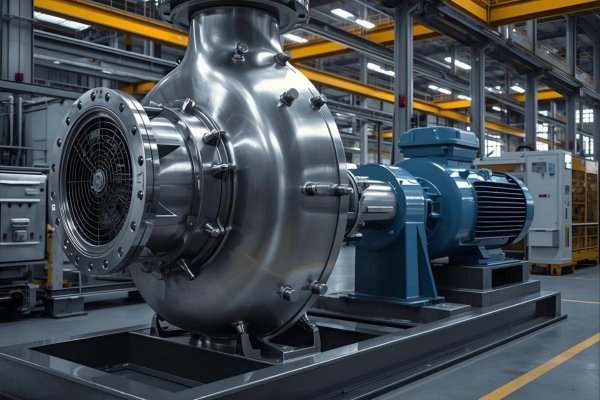
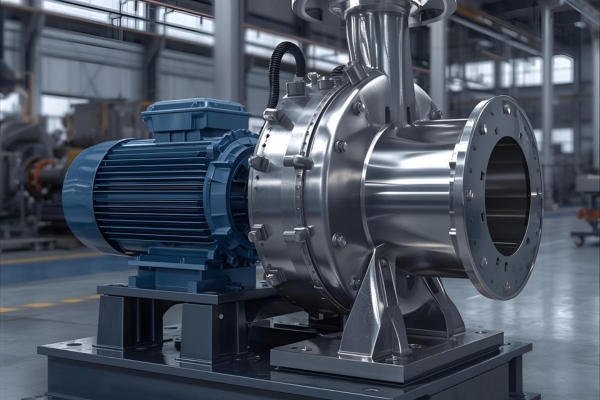
About Our Centrifugal Pumps
Our centrifugal pumps are engineered for continuous, trouble free operation in demanding process conditions. Every centrifugal pump is manufactured in our Ahmedabad facility with carefully selected materials, strict quality checks and performance testing before dispatch.
- Available in metallic and non metallic construction for corrosive and non corrosive liquids
- End suction and back pull out design for easy maintenance
- Wide range of capacities, heads and temperatures
- Heavy duty bearings and robust shaft design for long service life
- Interchangeable parts for reduced inventory and downtime
Whether you are looking for a single centrifugal pump for a small plant or a complete set of centrifugal pumps for a large process, Rinku Engineers provides optimized solutions with quick delivery and reliable after sales support.
Key Highlights
- Over 25 years of manufacturing experience
- Designs suitable for clear, slurry and corrosive liquids
- Proven performance in continuous process industries
- Serving Indian and global customers as a dependable centrifugal pump supplier
What Is a Centrifugal Pump and How It Works
A centrifugal pump is a rotodynamic pump that uses an impeller to add velocity to the liquid and convert this velocity into pressure at the pump outlet. Liquid enters the pump through the suction nozzle, flows to the impeller eye and is accelerated between the impeller vanes. The casing then converts this velocity into useful pressure energy, delivering the liquid at the required head and flow rate.
Because of this simple yet efficient working principle, centrifugal pumps are widely used in industrial, agricultural and utility applications. As a dedicated centrifugal pumps manufacturer, Rinku Engineers optimizes impeller design, casing shape and material selection to achieve high efficiency and low power consumption.
Centrifugal Pumps Range at Rinku Engineers
We manufacture a wide range of centrifugal pumps for different duties, from clean water transfer to aggressive chemical handling.
| Pump Model / Series | Type of Centrifugal Pump | Capacity (m3/hr) | Head (m) | Material of Construction | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AYUSH Process Pump | End suction horizontal centrifugal pump | 5 to 500 | 10 to 150 | CI / SS 304 / SS 316 | Chemical process, utilities, general industry |
| AYUSH Chemical Pump | Chemical duty centrifugal pump | 3 to 250 | 15 to 120 | SS 316 / Alloy steel | Acids, alkalis, corrosive chemicals |
| AYUSH Polypropylene Pump | Non metallic centrifugal pump | 2 to 60 | 5 to 45 | PP / FRP | Highly corrosive liquids, pickling plants |
| AYUSH Multistage Feed Pump | Horizontal multistage centrifugal pump | 3 to 180 | 40 to 250 | Cast steel / Stainless steel | Boiler feed, high pressure circulation |
| AYUSH Slurry Handling Pump | Centrifugal slurry pump | 10 to 600 | 10 to 90 | High chrome alloy / Rubber lined | Slurry, mud, effluent, abrasive media |
| AYUSH Self Priming Pump | Self priming centrifugal pump | 5 to 120 | 6 to 45 | CI / SS | Loading, unloading, transfer from underground tanks |
The above table gives an overview of our major centrifugal pumps range. Custom engineered centrifugal pump configurations are also available on request.
General Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Range | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Type | Single and multistage centrifugal pumps | End suction, back pull out, vertical, self priming |
| Capacity | Up to 600 m3/hr | Depending on pump model and application |
| Head | Up to 250 m | Single and multistage options |
| Temperature | -20°C to 180°C | With suitable materials and sealing arrangements |
| Speed | 1450 / 2900 rpm | Standard IEC motors, other speeds on request |
| Sealing | Gland packing / Mechanical seal | Selection as per process fluid and operating conditions |
| Testing | Hydrostatic and performance tests | As per relevant IS / ISO standards |
As a responsible centrifugal pump manufacturer in Ahmedabad, we can also design centrifugal pumps for special liquids, higher temperatures and different standards on request.
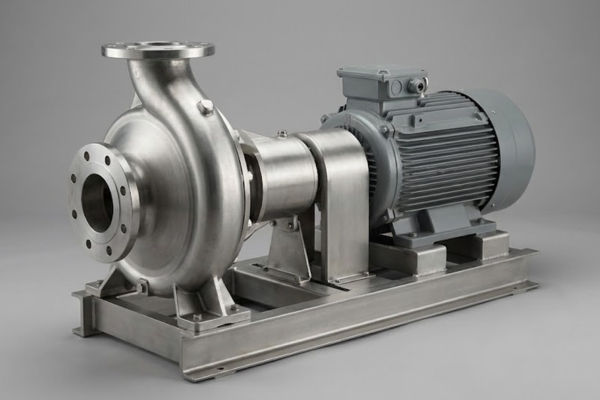
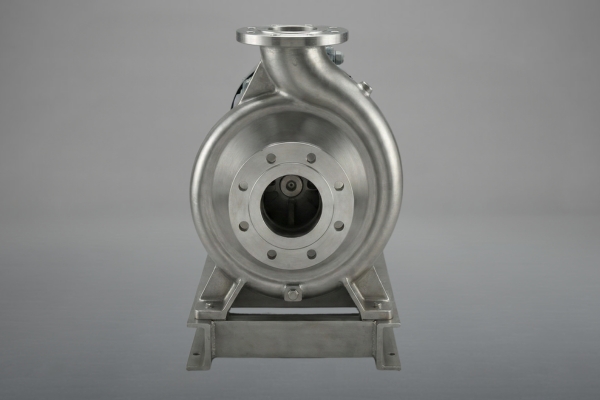
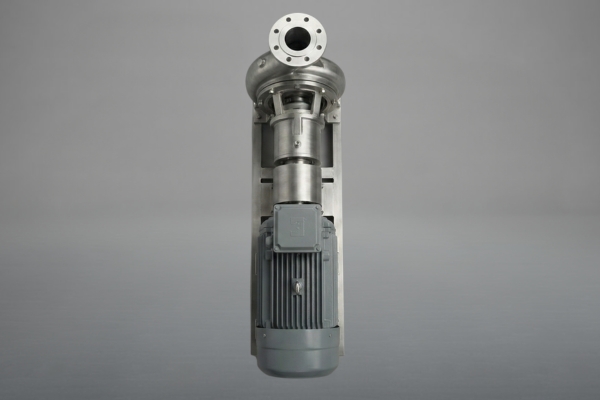



Industries We Serve
Our centrifugal pumps are installed in a wide range of industries and process plants.
- Chemical and petrochemical plants
- Pharmaceutical and API units
- Paper, pulp and textile industries
- Food, edible oil and dairy processing
- Water treatment and effluent treatment plants
- Sugar, steel and power plants
- Fertilizer and agro chemical units
- General industrial and utility water supply
Advantages of Rinku Engineers Centrifugal Pumps
- High efficiency hydraulic design for lower energy consumption
- Rugged construction for long service life and reduced breakdowns
- Wide choice of metallurgy to handle corrosive and abrasive liquids
- Standardized components for easy maintenance and quick spares availability
- In house design, machining and assembly for consistent quality
- Field proven performance in thousands of installations
- Technical support from selection to commissioning
These benefits make Rinku Engineers a preferred centrifugal pumps supplier in Ahmedabad for OEMs, project consultants and end users.
Centrifugal Pump Manufacturer, Supplier and Exporter in Ahmedabad
Strategically located in Vatva GIDC, Ahmedabad, Rinku Engineers serves as a reliable centrifugal pump supplier in Ahmedabad and across Gujarat with quick deliveries and prompt service. Our strong distribution network and export capabilities also make us a trusted centrifugal pump exporter in Ahmedabad for customers in the Middle East, Africa and Asian markets.
As an experienced centrifugal pumps manufacturer, we understand local as well as international standards and documentation requirements. From enquiry to dispatch, every stage is handled by our qualified team to ensure that your centrifugal pump performs as expected at site.

How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump
Choosing the correct centrifugal pump is essential for reliable and efficient operation. Our engineers help you select the right model based on the following data:
- Type of liquid and its properties (corrosive, abrasive, viscosity, specific gravity)
- Required flow rate (m3/hr or LPM)
- Total head, suction head and discharge head
- Operating temperature and pressure
- Available motor power and voltage
- Site conditions and installation constraints
Share your application details with us and we will recommend the most suitable centrifugal pump for long term performance and low operating cost.
Frequently Asked Questions about Centrifugal Pumps
1. What is the main advantage of centrifugal pumps?
Centrifugal pumps have a simple design, compact size and smooth, pulsation free flow. They are easy to install, require low maintenance and can handle a wide range of liquids, which is why most process industries prefer centrifugal pumps for continuous operation.
2. In which areas are Rinku Engineers centrifugal pumps used?
As a leading centrifugal pump manufacturer and supplier in Ahmedabad, our pumps are used in chemical process plants, ETP and STP plants, food and oil refineries, textile and paper mills, boiler feed systems, cooling water systems and many other industrial and utility applications.
3. Do you export centrifugal pumps outside India?
Yes. Rinku Engineers is an established centrifugal pumps exporter in Ahmedabad, supplying pumps to customers in the Middle East, Africa and other regions. We provide export quality packing, documentation and technical support for international shipments.
4. Can you provide customized centrifugal pump solutions?
We can customize centrifugal pumps in terms of materials, sealing, base frame, coupling guard, special coatings and accessories based on project or OEM requirements. Our design team works closely with customers and consultants to deliver tailor made solutions.








